Gold: $5,234.20 ▲ $176.39 Silver: $114.99 ▲ $7.38 Platinum: $2,676.68 ▼ $190.27 Palladium: $1,962.41 ▼ $116.62
Understanding industry terminology is essential for making informed investment decisions in precious metals. Furthermore, this comprehensive glossary covers the key terms you’ll encounter when buying gold coins, silver coins, and bullion products. Moreover, bookmark this page as a quick reference guide for your IRA investments and coin purchases.
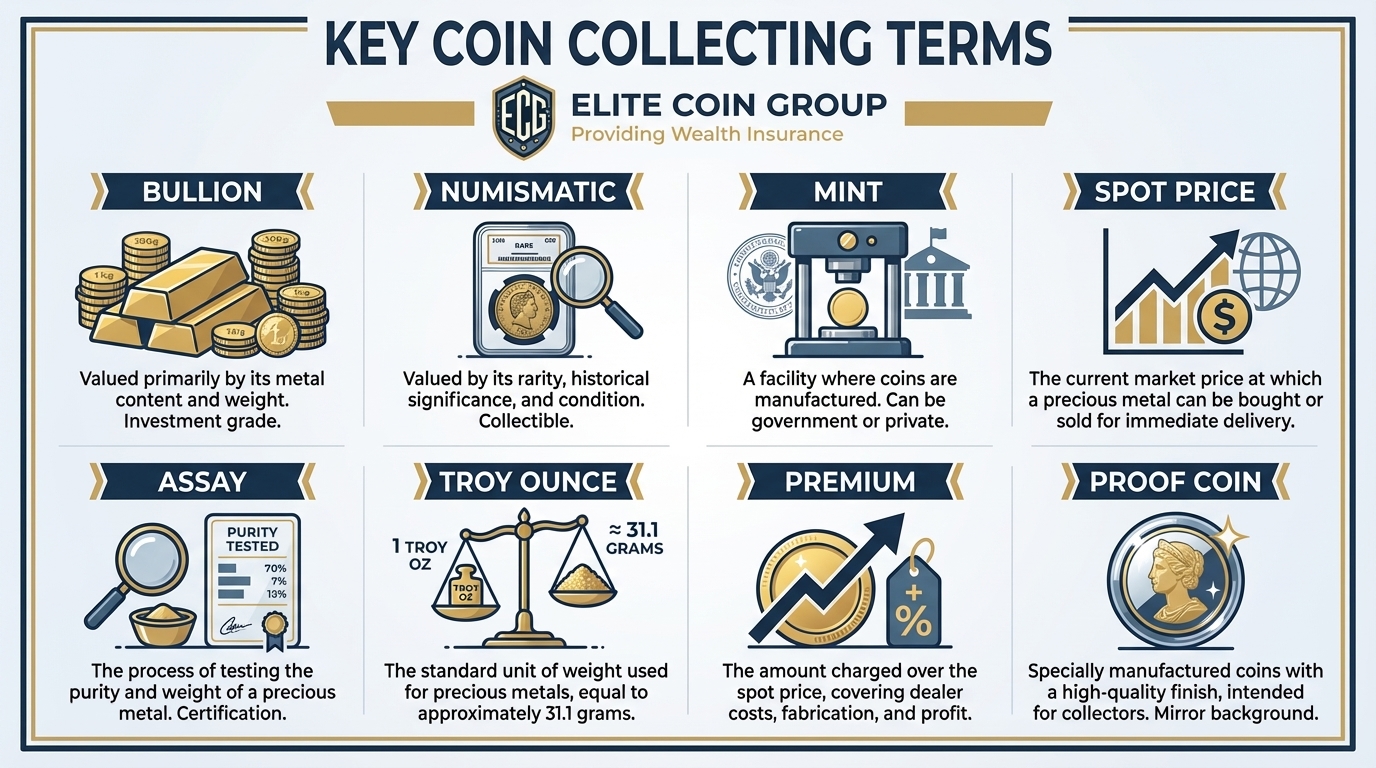
First and foremost, bullion refers to precious metals such as gold, silver, platinum, and palladium in the form of bars, ingots, or coins. Investors value these metals by weight and purity rather than their face value as currency. As a result, investors typically buy and sell bullion for investment purposes, gaining a tangible asset that acts as a hedge against inflation and economic instability.
Additionally, the spot price represents the current market price at which buyers and sellers can trade a particular precious metal for immediate delivery. Dealers use it as a critical benchmark for pricing bullion products. Moreover, the spot price fluctuates throughout the trading day based on supply and demand dynamics in global precious metals markets.
Meanwhile, the premium represents the amount by which the price of a bullion coin or bar exceeds the spot price of the metal it contains. Essentially, this markup covers manufacturing costs, distribution, and dealer margins. However, premiums can vary based on factors such as product demand, minting quality, and market conditions.
Notably, the precious metals industry uses the troy ounce as its standard unit of weight. To clarify, one troy ounce equals approximately 31.1035 grams, making it slightly heavier than a standard ounce (28.3495 grams). The industry has relied on this measurement for centuries, and it remains crucial in the pricing and trading of bullion.
In contrast to bullion, numismatic coins derive their value from factors beyond the metal content. For example, rarity, historical significance, condition, and collector demand all play important roles in determining value. Consequently, these coins often command a premium compared to their bullion counterparts due to their unique characteristics and appeal to collectors.
Furthermore, a mint operates as a facility where governments authorize coin production. Mints manufacture bullion coins, commemorative coins, and circulating currency. For instance, well-known mints include the United States Mint, the Royal Canadian Mint, and the Perth Mint.
Similarly important, an assay tests and determines the purity and composition of a precious metal. Certified assayers perform this essential process to verify the authenticity and value of bullion products. Official mints, private mints, or independent assay offices can conduct these certifications.
Finally, mints create proof coins using a special minting process that involves multiple strikes and highly polished dies. This process produces coins with sharp details and a mirror-like finish. Mints typically produce proof coins in limited quantities, and collectors highly prize them for their superior craftsmanship and aesthetic appeal.
Additionally, explore these resources to deepen your understanding of precious metals investing:
Have questions about a term you don’t see here? Our numismatic experts are ready to help you navigate the world of precious metals investing.